Indirect finance involves intermediaries facilitating transactions between lenders and borrowers.

Credit: homework.study.com
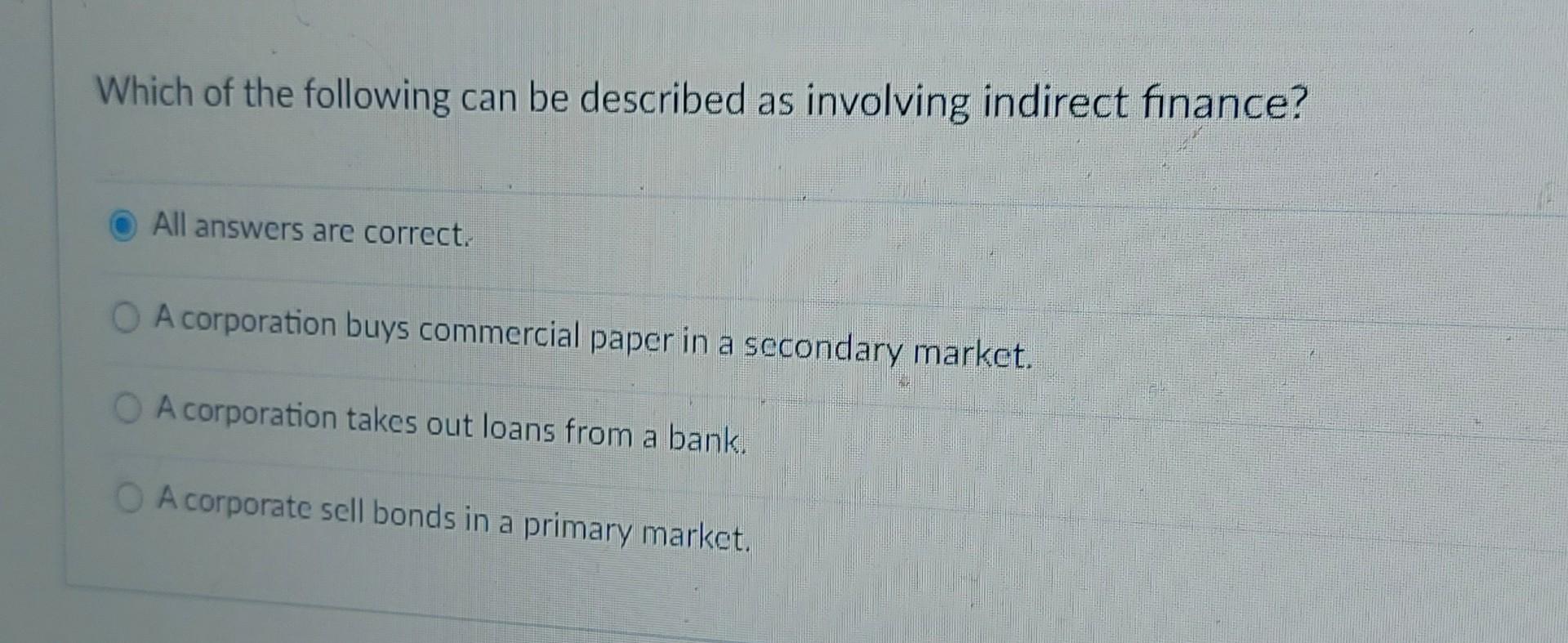
Credit: www.chegg.com
Understanding Indirect Finance
Indirect finance is a process where financial institutions act as middlemen, providing a link between those who have funds to lend and those who need funds.
Examples Of Indirect Finance:
| Indirect Finance | Description |
|---|---|
| Bank Loans | When banks lend money to individuals or businesses on behalf of depositors. |
| Insurance Companies | Insurance companies investing premiums in various financial instruments. |
| Mutual Funds | Pooling funds from investors to invest in diversified portfolios. |
Benefits of Indirect Finance:
- Diversification of risk for lenders and borrowers.
- Increased liquidity in financial markets.
- Access to a wider range of investment opportunities.
Challenges of Indirect Finance:
- Dependency on intermediary institutions.
- Potential for higher transaction costs.
- Risk of agency problems in fund management.
Indirect finance plays a crucial role in the global economy by facilitating the flow of funds between savers and borrowers.
Final Thoughts
Understanding indirect finance is essential for investors, borrowers, and financial institutions to make informed decisions and navigate the complexities of the financial system.
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is Indirect Finance?
Indirect finance involves transactions through intermediaries like banks rather than directly between borrowers and lenders.
How Does Indirect Finance Work?
In indirect finance, financial institutions act as intermediaries to facilitate lending and borrowing activities between parties.
Why Is Indirect Finance Important?
Indirect finance plays a crucial role in the economy by providing a channel for funds to flow between savers and borrowers.
What Are Examples Of Indirect Finance?
Examples of indirect finance include bank loans, mortgages, and investments in mutual funds or pension funds.
What Are The Benefits Of Indirect Finance?
Indirect finance offers diversification, risk management, and liquidity benefits to both lenders and borrowers in the financial system.