In marketing, utility refers to the value or benefit a product offers to customers. It encompasses the product’s usefulness, satisfaction, and the customer’s perception of the product’s worth.
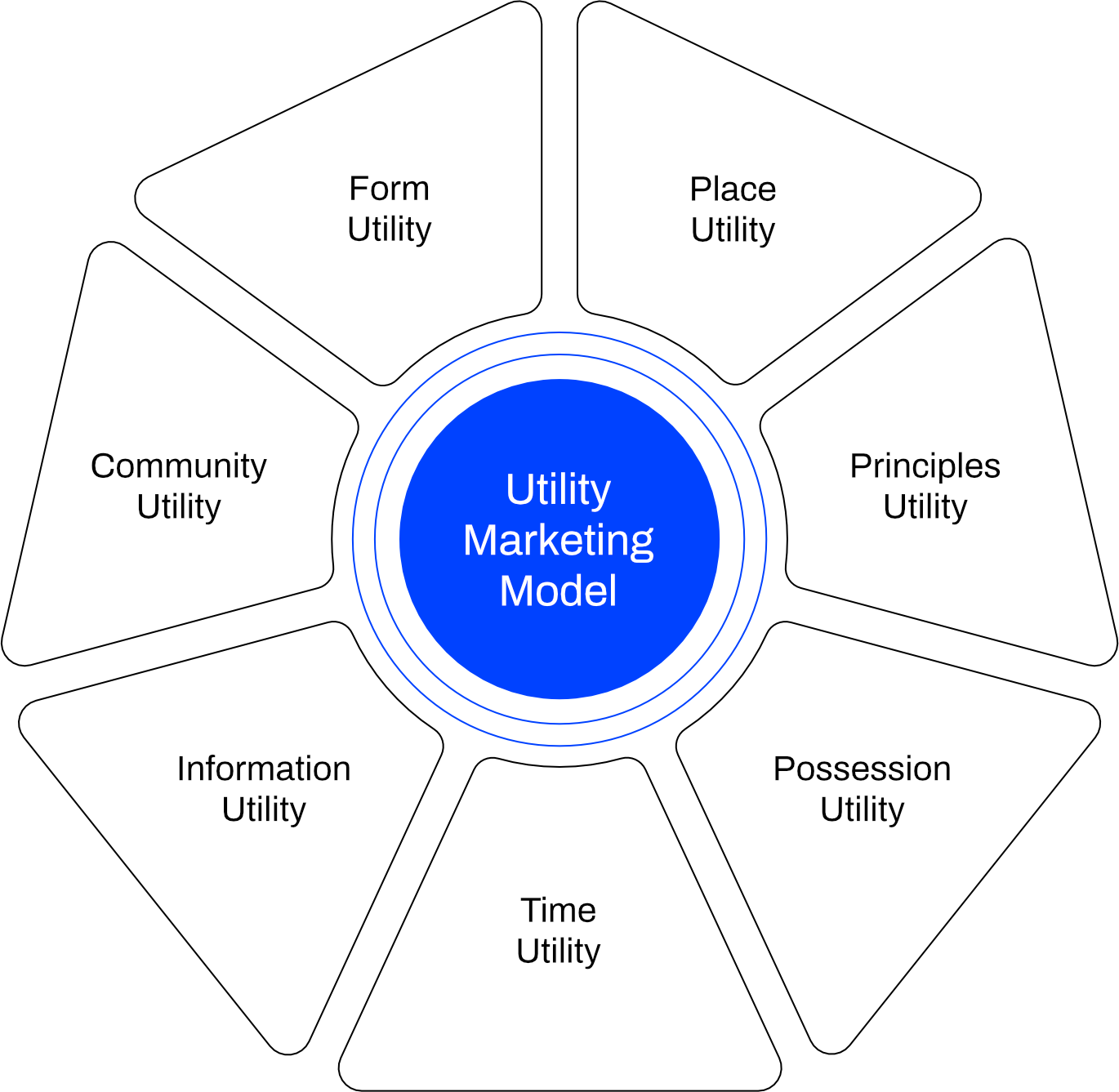
When customers buy a product, they do so with the expectation of receiving some form of utility from it. There are four types of utility in marketing: form utility, place utility, time utility, and possession utility. Form utility relates to the product’s features and design, while place utility refers to its availability.
Time utility pertains to the product’s availability at the right time, and possession utility deals with the ease of ownership. Understanding and delivering these utilities to the customers is essential for successful marketing strategies and customer satisfaction. By providing value and benefits, businesses can fulfill customer needs and wants, and ultimately improve their sales and market presence.
Credit: www.createutility.io
1. Defining Utility In Marketing
When it comes to marketing, utility plays a crucial role in determining the value a product or service provides to customers. In simple terms, utility refers to the usefulness or satisfaction that a customer derives from consuming a product or service. In the competitive world of marketing, understanding and delivering utility is essential for businesses to attract and retain customers. Let’s delve deeper into the concept of utility and its importance in marketing.
1.1 The Concept Of Utility
Utility in marketing can be categorized into four different types: form utility, time utility, place utility, and possession utility. Each type of utility focuses on a different aspect of a customer’s experience with a product or service.
Form Utility
Form utility refers to the value that customers derive from the physical characteristics or features of a product. It encompasses factors such as design, functionality, packaging, and quality. One example of form utility is a smartphone that not only meets the basic communication needs but also provides advanced features like a high-resolution camera or fingerprint recognition.
Time Utility
Time utility emphasizes the convenience and timeliness of a product or service. It is about providing customers with access to a product or service at the right time. For instance, online streaming platforms like Netflix offer time utility by allowing users to watch their favorite shows and movies whenever and wherever they want, eliminating the need to adhere to fixed broadcasting schedules.
Place Utility
Place utility focuses on making a product or service available at the right place or location for customers. It involves strategically positioning products or services in accessible locations to maximize convenience. An example of place utility can be seen in the establishment of retail stores in prime locations or the presence of vending machines in public spaces.
Possession Utility
Possession utility relates to the ease and convenience of owning or possessing a product or service. It includes factors such as affordability, financing options, and after-sales services. For instance, a car dealership offering flexible payment plans or warranty programs enhances possession utility as it makes owning a car more accessible and hassle-free for customers.
1.2 Importance Of Utility In Marketing
The concept of utility is of paramount importance in marketing for several reasons:
- Attracts Customers: Incorporating utility into products or services makes them more appealing and desirable to customers. By meeting their needs and providing unique value propositions, businesses can stand out in the competitive market.
- Fosters Customer Satisfaction: When customers perceive a high level of utility in a product or service, it enhances their satisfaction. Satisfied customers are more likely to become repeat customers and recommend the product or service to others, leading to increased sales and brand reputation.
- Competitive Advantage: Utility can serve as a competitive advantage, allowing businesses to differentiate themselves from rivals. By understanding customer preferences and aligning their offerings to maximize utility, businesses can gain an edge in the market.
- Creates Customer Loyalty: Utility contributes to building strong customer loyalty. Customers who consistently experience utility in their interactions with a brand are more inclined to develop loyalty towards the brand, resulting in long-term relationships and increased customer lifetime value.
In conclusion, utility in marketing is the driving force behind customer satisfaction, loyalty, and business success. By incorporating and optimizing the different types of utility, businesses can ensure their offerings provide genuine value to customers, ultimately leading to increased sales and profitability.
2. Types Of Utility
2. Types of Utility
2.1 Form Utility
Form utility refers to the value addition to a product by changing its form, making it more useful and attractive to consumers. For example, converting raw materials into finished goods creates form utility.
2.2 Time Utility
Time utility involves making a product available when consumers want to purchase it. This can be achieved through effective inventory management, seasonal sales, or offering products at convenient times for consumers.
2.3 Place Utility
Place utility focuses on making the products available at the right place, which aligns with consumer purchasing habits. It involves distribution channels, strategic location of retail outlets, and e-commerce platforms to reach a wider audience.
2.4 Possession Utility
Possession utility concerns the transfer of ownership or the right to use a product. This typically includes payment methods, financing options, and customer-friendly return policies to encourage consumers to possess the product.
3. Maximizing Impact Through Strategic Tools
Increase the impact of marketing strategies through the strategic use of utility, maximizing customer engagement and brand loyalty. Generate value-driven content and tools to enhance customer experience and drive conversions. Utilize utility in marketing to create meaningful connections and deliver tangible benefits to consumers.
Strategic tools play a vital role in maximizing the impact of marketing efforts. By strategically leveraging these tools, businesses can enhance their utility and reach their target audience more effectively.
3.1 Understanding Strategic Tools In Marketing
Strategic tools in marketing are instruments or techniques used to execute marketing strategies in a well-thought-out manner. These tools are designed to optimize marketing performance and achieve specific objectives.
3.2 Role Of Strategic Tools In Maximizing Utility
Strategic tools are essential for extracting maximum utility from marketing campaigns. They help businesses analyze data, plan strategies, and implement tactics that align with their goals, leading to increased effectiveness and efficiency.
3.3 Examples Of Strategic Tools For Maximizing Impact
- Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software
- Marketing automation platforms
- Competitive analysis tools
| Strategic Tool | Utility |
|---|---|
| CRM software | Enhances customer interactions and retention. |
| Marketing automation platforms | Streamlines marketing processes and improves lead generation. |
| Competitive analysis tools | Helps businesses stay ahead by understanding competitor strategies. |

Credit: www.techloyce.com
4. Implementing Strategic Tools In Marketing
In order to effectively promote products and engage with customers, businesses must implement strategic marketing tools. These tools enable companies to identify target audiences, develop comprehensive strategies, utilize digital marketing techniques, and evaluate and optimize their efforts. By incorporating these tools into their marketing approach, businesses can maximize their reach and effectiveness, ultimately driving success.
4.1 Identifying Target Audience And Market Trends
One of the critical aspects of successful marketing is identifying the target audience. By understanding who your customers are, their needs, preferences, and behaviors, businesses can tailor their marketing efforts to effectively resonate with their desired demographic. In addition, keeping an eye on market trends is essential to stay ahead of the competition and adapt strategies accordingly. Businesses can leverage various market research tools, surveys, and data analysis to gain insights into their target audience and market trends.
4.2 Developing A Comprehensive Marketing Strategy
A comprehensive marketing strategy acts as a roadmap for businesses to achieve their marketing goals. It outlines the objectives, target audience, key messaging, channels, and tactics to be employed. By developing a well-thought-out strategy, businesses can streamline their marketing efforts and allocate resources effectively. This process involves conducting research, analyzing competition, and identifying unique selling points. A comprehensive strategy allows businesses to create a cohesive and consistent brand image, resulting in stronger customer engagement and brand loyalty.
4.3 Utilizing Digital Marketing Tools
In today’s digital age, leveraging online platforms and tools is crucial for successful marketing. Digital marketing offers a wide range of opportunities to reach and engage with customers, including social media, email marketing, content marketing, search engine optimization (SEO), and paid advertising channels. By utilizing these tools effectively, businesses can expand their reach, increase brand visibility, and drive targeted traffic to their websites. Online analytics tools also provide valuable insights into customer behavior and campaign performance, enabling businesses to optimize their digital marketing strategies.
4.4 Evaluating And Optimizing Marketing Efforts
Regular evaluation and optimization of marketing efforts are essential for ongoing success. By closely monitoring campaign performance, businesses can identify what works and what needs improvement. Key performance indicators (KPIs) such as conversion rates, click-through rates, and customer engagement metrics can provide valuable feedback. By analyzing this data, businesses can make data-driven decisions and refine their marketing strategies accordingly. Optimization involves making iterative adjustments to campaigns, messaging, targeting, and channels to achieve better results. This continuous process ensures that marketing efforts remain relevant and effective in an ever-evolving market.
5. Case Studies: Successful Utility-driven Marketing Campaigns
Discover real-world examples of successful utility-driven marketing campaigns through engaging case studies. Learn how brands leverage utility in marketing to provide value and meet customer needs effectively. Gain insights into strategies that have proven results in delivering impactful and customer-centric campaigns.
Utility-driven marketing campaigns have emerged as a powerful strategy that focuses on providing value and usefulness to customers. These campaigns not only help brands establish a strong connection with their audience but also foster long-term loyalty. By going beyond traditional advertising, companies can create a lasting impact on consumers’ lives. In this section, we will explore two case studies that demonstrate the effective use of utility in marketing.
5.1 Case Study 1: Company X’s Use Of Utility In Marketing
Company X, a leading player in the tech industry, recognized the importance of utility in driving customer engagement. To achieve this, they developed a mobile app that provided users with expert tips, tutorials, and personalized recommendations based on their preferences. The app was designed to address users’ pain points and empower them to make informed decisions. By serving as a one-stop resource, Company X positioned itself as a trusted advisor in their field.
The key to Company X’s success was the seamless integration of their product offerings and utility-driven marketing. By connecting their app with their core products, they not only added value to customers’ lives but also increased the adoption of their solutions. This approach helped them build a loyal customer base and establish themselves as industry leaders.
5.2 Case Study 2: Brand Y’s Innovative Approach To Maximizing Impact
Brand Y, a renowned fashion brand, embraced an innovative approach to utility-driven marketing by leveraging user-generated content (UGC). They invited their customers to share their personal style and fashion tips on social media using a unique hashtag. Brand Y then curated the best submissions on their website, creating a community-driven platform that showcased real people and their authentic experiences.
This UGC campaign not only encouraged engagement but also instilled a sense of inclusivity among customers. By featuring diverse individuals and celebrating their unique styles, Brand Y resonated with a wider audience. This approach helped them maximize their impact by turning their customers into brand ambassadors, driving word-of-mouth marketing and increasing brand awareness.

Credit: www.marketing91.com
Frequently Asked Questions
What Is An Example Of Utility?
An example of utility is electricity, which powers our homes and appliances for daily tasks.
What Are The 4 Types Of Utility And Examples?
The four types of utility are form, time, place, and possession. Form utility is adding value by transforming raw materials into a finished product. Time utility refers to making a product available when it’s needed. Place utility involves making the product available where it’s needed.
Possession utility is the value added by facilitating the purchase and use of a product.
What Is Utility And Demand In Marketing?
Utility in marketing refers to the satisfaction that a product or service provides to consumers. Demand refers to the desire, willingness, and ability of customers to purchase that product or service. These factors play a crucial role in determining the success of marketing strategies and influencing consumer behavior.
What Is Utility Model In Marketing?
A utility model in marketing refers to a practical and functional invention that provides a new and useful solution. It is a legal protection that allows inventors to exclude others from using, manufacturing, or selling their invention without permission. Utility models are often used to protect minor inventions with short-term validity.
What Role Does Utility Play In Marketing Strategy?
Utility in marketing refers to the value a product or service provides to customers.
Conclusion
Understanding the concept of utility in marketing is crucial for businesses to meet customer needs. By creating products and services that offer high utility, companies can maximize customer satisfaction and loyalty. As a result, businesses can gain a competitive edge in the market and drive long-term success.
Embracing utility in marketing strategies can lead to better customer relationships and increased profitability.