Marketing is not one of the basic areas of finance. The three primary areas are corporate finance, investments, and financial markets and institutions.
Finance is a multifaceted field that forms the backbone of economic activities. It focuses on the management of money, including acquiring, investing, and spending. Corporate finance deals with how companies manage their capital structure and funding to increase value and ensure financial stability.
Investments surround the decision-making process involving asset allocation and portfolio management. Financial markets and institutions encompass the systems and organizations that facilitate transactions in financial securities and instruments. These basic fields of finance interlink to support the global economy’s functioning, and professionals must often collaborate across these domains to achieve optimal financial outcomes. Understanding these core areas is crucial for anyone seeking to navigate the intricacies of the financial landscape.
Decoding The Basic Areas Of Finance
Understanding finance is like piecing together a giant puzzle. Each piece has its place. Missing one can confuse the entire picture. In the world of finance, certain areas are key. These form the foundation of a healthy financial system. Knowing these areas helps in making smart money decisions.
Key Components Of Finance
Finance revolves around planning, creating, and managing money. Let’s break down these components:
- Personal Finance: It’s all about managing your money. This includes saving, spending, and planning for the future.
- Corporate Finance: This focuses on how businesses handle their funds. They invest, budget, and plan for growth here.
- Public Finance: This deals with government spending. It also involves taxes and budgeting for public projects.
These areas serve as the building blocks of finance. They help us steer through financial waters.
Common Misconceptions
Understanding finance means also busting myths. Here are some areas often confused with finance:
| Not Finance Areas | Reasons |
|---|---|
| Economics | It’s about the economy as a whole, not just money management. |
| Accounting | It involves recording financial transactions, not planning or managing. |
Remember, finance is broader than just bookkeeping or the economy. It’s a complex field with specific focus areas.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dodd-frank-financial-regulatory-reform-bill.asp-final-5ae832d396f345ee8706cdac55670ebf.png)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Personal Vs. Corporate Vs. Public Finance
Understanding the spheres of finance is crucial for navigating the financial world. Three prominent pillars stand tall: personal, corporate, and public finance. Each plays a unique role in the economic ecosystem. But which of these is not a primary area of finance? This section delves into each domain, highlighting key distinctions, and revealing the outlier that intrigues many.
Individual Financial Management
Personal finance is all about managing money for a person or a family. It covers:
- Budgeting – Planning spending wisely
- Saving – Putting money aside for the future
- Investing – Growing wealth over time
- Retirement Planning – Preparing for the golden years
This area focuses on achieving personal financial goals, whether short-term needs or long-term aspirations like home ownership or retirement.
Business Finance Essentials
Corporate finance revolves around the financial activities of companies. Main aspects include:
- Capital Structure – Deciding the right mix of debt and equity
- Financial Reporting – Presenting company finances transparently
- Investment Analysis – Evaluating opportunities for growth
- Cash Flow Management – Ensuring liquidity for operations
Businesses strive to maximize the shareholder value through prudent financial management and investment strategies.
Government Financial Operations
Public finance details how government manages income and expenses. Critical components are:
| Budgeting | Spending | Funding |
|---|---|---|
| Allocating resources effectively | Executing public projects | Generating revenue through taxes |
It aims to provide public services, maintain economic stability, and manage the nation’s economic resources sensibly.
Exploring Uncommon Finance Categories
When you think about finance, certain words likely come to mind—banks, stocks, or maybe even debt. Yet, there are areas that don’t often make the list. Let’s dive into these less-discussed categories. They may not be the basic areas of finance, but they hold their own unique importance.
Behavioral Finance
Behavioral finance looks at how psychology impacts financial markets. This field asks why we make money decisions. It is not your regular finance topic, but it shapes many of our choices.
- Emotions: They can lead us to buy or sell at the wrong time.
- Biases: They affect how we view investment risk.
- Mental Accounting: It’s why we treat different money sources differently.
Think of behavioral finance as the ‘why’ behind the ‘what’ in money matters.
Social Finance
Then we have social finance—it combines investing with social benefits. This area looks past the cash to see the wider impact. It is finance plus a heart.
| Term | Meaning |
|---|---|
| Socially Responsible Investing (SRI) | Choosing stocks that match personal values. |
| Impact Investing | Funding projects with a positive impact. |
| Microfinance | Small loans to help the less fortunate. |
Social finance highlights how money can be a force for good.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/Pro-Forma-V2-c9d1a7bd7843405e8de36c734e910f44.jpg)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Investments And Risk Management
Understanding where finance does not venture is just as crucial as knowing its main functions. Finance typically covers a wide array of activities, including banking, investments, and risk management, yet not all areas are finance’s domain. The basics of finance revolve around managing money and assets. Investments often shape the backbone of financial growth strategies, while risk management seeks to protect assets from potential downturns. Our focus here is to demystify these two interconnected areas.
Investment Strategies
Every investor has unique goals and resources. Hence, there is a variety of investment approaches to consider. Investment strategies guide decisions on where to put money to work.
- Stocks: Owning a piece of a company and potentially earning dividends.
- Bonds: Lending money to entities in exchange for interest payments.
- Real Estate: Investing in property to gain rental income or capitalize on appreciation.
- Mutual Funds: Pooling funds to buy a diversified portfolio managed by professionals.
Create a plan that aligns with your risk tolerance and financial goals. Diversification across different asset classes is a key tactic to reduce risk.
Mitigating Financial Risks
In finance, the potential for loss is a constant. Mitigating financial risks is essential to safeguard investments. Keeping risks in check involves several strategies, detailed below:
| Risk Type | Strategy |
|---|---|
| Market Risk | Diversify investments across various sectors and asset types. |
| Credit Risk | Analyze credit reports and invest in high-grade bonds. |
| Liquidity Risk | Hold assets that can be easily converted to cash. |
| Operational Risk | Use insurance and robust operational controls. |
Each strategy must be tailored to fit the specific needs of the portfolio. Regularly revisiting and adjusting strategies is key to keeping risks at bay.
Financial Intermediation And Markets
Understanding finance means knowing how money moves. Among the Basic Areas of Finance, financial intermediation and markets are key. They work together like gears in a clock. But, is there something that doesn’t fit in this category? Let’s find out by diving into the roles and functions of this financial engine.
Role Of Banks And Institutions
Banks stand as sturdy pillars in the financial system. They move money from savers to borrowers. This is a main role, but not the only one. Banks also provide security and speed in transactions. Financial institutions like insurance companies and pension funds work similarly. They collect premiums or contributions and invest them where needed.
- Safety of deposits
- Providing loans to businesses and individuals
- Facilitating investments for growth
- Offering payment services for ease
Functioning Of Financial Markets
Financial markets act as the stage where money performs. They are the platforms for buying and selling securities. Stocks, bonds, and other assets change hands here. Markets decide prices based on supply and demand.
| Type of Market | Function |
|---|---|
| Stock Market | Trading company shares |
| Bond Market | Dealing in government and corporate debt |
| Commodities Market | Buying and selling raw materials |
| Forex Market | Exchanging currencies |
Markets offer liquidity and transparency. They make it easy to buy or sell assets any time. They also show clear prices for all to see.
- Liquidity means selling fast without losing value.
- Transparency means everyone can see all prices and trades.
Identifying Non-fundamental Finance Areas
Fundamentals define the core of finance. Yet, some areas don’t fit the basic mold. We’ll explore non-essential finance sectors. These areas might not be the first you learn, but they’re creating buzz. Let’s dig into the emerging and peripheral domains.
Emerging Finance Subfields
Finance never stops evolving. New subfields emerge as technology advances. We see unique intersections of finance with other industries. This brings about specialties once not considered finance.
- FinTech: Technology transforms financial services.
- Crypto Finance: Digital currencies create new finance models.
- Green Finance: Combining sustainability with investment.
- Behavioral Finance: Psychology’s role in financial decisions.
These subfields are gaining ground. They join traditional areas like banking, investments, and risk management. Do they define finance basics? Not yet. They are potential future staples.
Outside The Core Financial Spectrum
Some areas touch finance only at their boundaries. They seem distant from the core principles. Yet, they impact financial decisions and strategies.
| Non-Fundamental Area | Description |
|---|---|
| Real Estate: | Deals with property. |
| Art Investment: | Fuses culture with capital growth. |
| Philanthropic Finance: | Finance with a heart for non-profit purposes. |
| Educational Finance: | Money management in schools and universities. |
These areas might not fall directly under finance. They live on its edges. Yet, understanding them can give you a broad view of financial ecosystems.
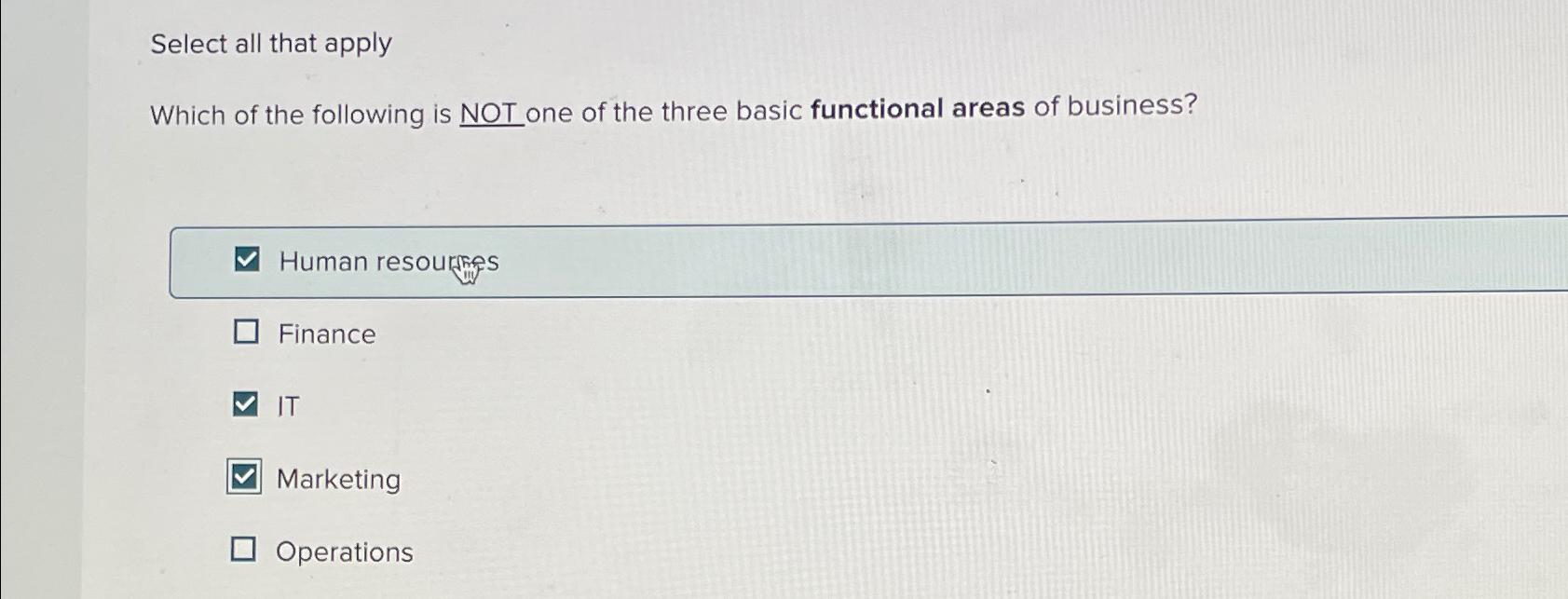
Credit: www.chegg.com
Frequently Asked Questions For Which Of The Following Is Not One Of The Basic Areas Of Finance?
What Are The 4 Areas Of Finance?
The four main areas of finance are corporate finance, investments, financial markets and institutions, and international finance.
Which Of The Following Is Not One Of The Basic Corporate Finance Functions?
Market research is not one of the basic corporate finance functions. Basic functions include capital budgeting, capital structure, and working capital management.
Which Are The Four Basic Areas Of Finance Which Are Listed Below?
The four basic areas of finance are corporate finance, investments, financial markets and institutions, and international finance.
Which One Of These Is Not One Of The Four Basic Financial Statements Quizlet?
The cash flow projection is not one of the four basic financial statements.
What Are Basic Finance Areas?
The basic areas of finance encompass three main categories: personal finance, corporate finance, and public (government) finance.
Conclusion
Understanding the basic areas of finance is crucial for sound economic decision-making. We’ve clarified which elements do not fit the finance category, aiding your knowledge growth. Keep expanding your financial literacy to navigate investments, budgeting, and resource allocation with confidence.
Stay informed and make savvy choices for a secure financial future.