Amsterdam dominated European trade and finance in the early seventeenth century. This Dutch city became the preeminent commercial hub of the era.
During the early 1600s, Amsterdam emerged as the epicenter of trade and finance in Europe, surpassing other cities with its innovative financial instruments and bustling port. The establishment of the Amsterdam Stock Exchange in 1602 marked the birth of modern capitalism and positioned the city as the leader in global trade.
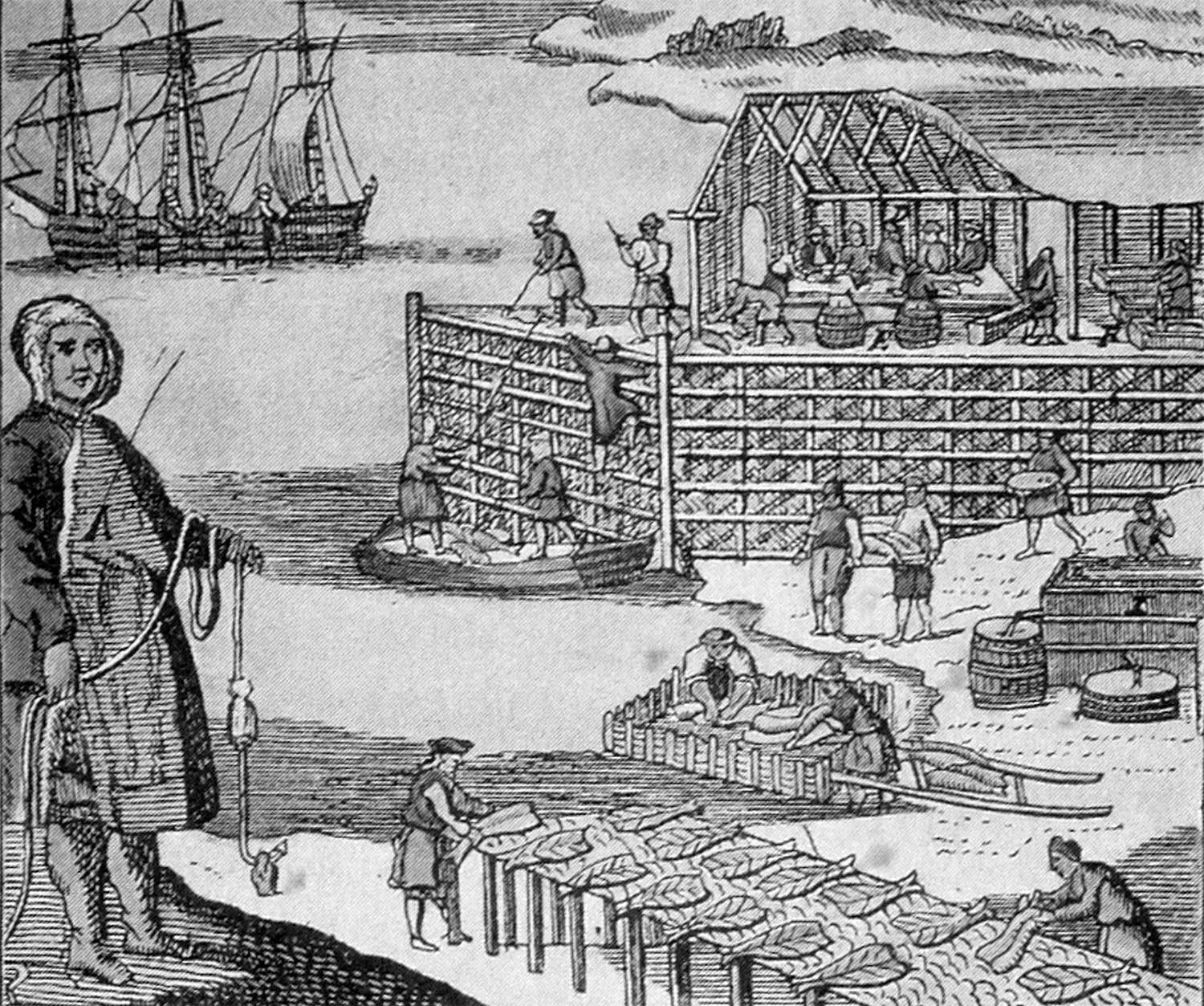
Merchants and financiers flocked to Amsterdam, drawn by its strategic location, which facilitated the Dutch East India Company’s far-reaching trade routes. This commercial vibrancy attracted investors and saw the introduction of groundbreaking financial products like stocks and bonds. The economic boom transformed the city into a rich cultural center, paving the way for the Dutch Golden Age. As the nexus of commerce in the seventeenth century, Amsterdam’s legacy continues to influence the financial markets of today.

Credit: monthlyreview.org
Early Centers Of Power And Commerce
In the tapestry of history, certain cities emerge as epicenters of power and commerce, reshaping the economic landscape with their might. In the dawn of the seventeenth century, a particular European city stood at the pinnacle of such transformation, becoming the heart of trade and finance. This city’s booming marketplace and financial influence were unprecedented during this era.
Influence Of Geographic Position
Location is key in the flowering of any city’s commercial dominance. The city in question, strategically located, became a crossroads for merchants and financiers. Its borders opened to vast oceans, leading to an influx of wealth and resources. This optimal position fostered immense trade opportunities and economic growth.
Trade Routes And Economic Success
The veins of trade routes running through this city pulsated with goods from around the globe. Lucrative trade agreements and a robust network of commerce formed the bedrock of its financial success. Here are some key factors that contributed:
- Access to the seas: Enabled expansive maritime trade.
- Trade networks: Connected to key regions of Europe and beyond.
- Merchants and bankers: Forged the city’s opulence through savvy dealings.
This combination of strategic geographic positioning and masterful command of trade routes ushered in an era of unmatched economic prosperity. It created a blueprint of success for cities vying for power and commerce supremacy.

Credit: en.wikipedia.org
Amsterdam’s Rise To Economic Stardom
The early seventeenth century heralded a new era for European trade and finance. Amsterdam emerged as the epicenter of this economic revolution. Its strategic location and innovative approaches to business catapulted the city to the forefront of wealth and influence. Businessmen descended upon its bustling docks; Amsterdam was the place to be for ambitious traders and savvy financiers alike.
The Dutch East India Company
The legendary Dutch East India Company, or VOC, played a pivotal role in Amsterdam’s ascendancy. Founded in 1602, the VOC was the world’s first multinational corporation and the first to issue stock. It dominated global trade, pioneering routes to exotic markets in the East Indies. The wealth it generated flowed through Amsterdam, enriching the city and its people.
- Monopolized Spice Trade
- Pioneered International Trade Routes
- Introduced Stock Trading
Innovations In Trade And Finance
Innovation was the rocket fuel of Amsterdam’s economic boom. The city revolutionized the world of finance with the establishment of the Amsterdam Stock Exchange, the world’s first. Traders flocked to the bustling financial markets, eager to invest in thriving industries.
- First Stock Exchange: Facilitated trading of VOC shares
- Banking System: Offered loans and managed international transactions
- Insurance: Protected investments and shipments
These advancements weren’t just about making money; they transformed Amsterdam into the heart of the global economy.
London’s Financial Revolution
During the early seventeenth century, a pivotal shift occurred in Europe’s trade and finance. London emerged as a powerhouse, reshaping the economic landscape. This revolution pivoted on two major developments: the creation of the Bank of England and the expansion of the English East India Company. Let’s delve into how these two entities fostered an environment for prosperity and dominance in global markets.
The Formation Of The Bank Of England
In the bustling heart of London, a financial institution was born. The Bank of England set the stage for economic stability. Established in 1694, this entity was pivotal in managing the nation’s debt. It was also instrumental in issuing reliable paper money. Below is a simple table showcasing the key functions of the Bank of England:
| Function | Description |
|---|---|
| Debt Management | Handle government debt, ensuring financial stability. |
| Monetary Stability | Issue banknotes, controlling currency supply. |
| Lender of Last Resort | Provide emergency funds to banks in crisis. |
The Bank of England was not just a bank; it was a revolution. It brought trust to banking and set a model for the world to follow.
Impact Of The English East India Company
The English East India Company’s clout in trade was equally transformative. As a commercial venture, it paved the way for Britain’s global dominance in trade. It traded in exotic commodities like spices, silk, and tea. This company did not only trade. It built an empire.
- Trade Monopoly: Held exclusive rights to trade with the East Indies.
- Political Power: Exerted influence on British and foreign policies.
- Economic Impact: The company’s success bolstered London’s economy.
The English East India Company fostered a web of global commerce. It linked London to the far corners of the world. Its impact reverberates through history, marking London as a center of finance and trade.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/dotdash-brief-history-international-trade-agreements-v2-2d7ef50e8498475e927985609a9d0308.jpg)
Credit: www.investopedia.com
Venice And Genoa: Decline Of Mediterranean Hegemony
For centuries, Venice and Genoa stood as colossal powers in European trade and finance. Their strategic locations bridged the East to the West. Wealth flowed through their ports in mighty currents. Yet, by the early seventeenth century, these shining beacons of Mediterranean might began to flicker and fade. Their storied pasts could not shield them from the tides of change. Let’s delve into the reasons their influence diminished.
Impact Of New Trade Routes
The Age of Exploration opened worldwide sea lanes. Explorers discovered faster, more direct routes to Asia. Mighty ocean-going ships reached the Americas. These new trade routes around Africa and across the Atlantic proved to be more efficient. Trade giants Venice and Genoa lost their monopoly. Eastern spices and silks now bypassed Mediterranean intermediaries. The wealth that once flowed through Italian city-states started to ebb.
- New maritime technology outpaced Mediterranean ships.
- Portugal and Spain spearheaded new trade ventures.
- European interests shifted towards the Atlantic ports.
Shift Of Economic Power Northwards
The balance of economic clout began to tip. Northern cities rose to prominence.
- Amsterdam became a bustling port, rich in trade and finance.
- Antwerp emerged as a leading diamond and banking center.
- London established itself as a hub for global commerce and banking.
These northern hubs became the new nexus of European trade. Customary Mediterranean leaders watched their influence wane. The economic landscape remapped itself, setting the stage for modern capitalism.
Comparative Analysis Of Trading Capitals
Let’s delve into the bustling world of early 17th century trade. A time when cities vied for economic supremacy. Among those, Amsterdam emerged as a colossal force. London followed suit, showing signs of burgeoning financial strength.
Factors In Amsterdam’s Dominance
Amsterdam, a trade titan, owed its success to multiple factors:
- Strategic Location: Nestled at the delta of the Rhine and Ijssel rivers, Amsterdam became a magnet for goods.
- Innovative Financial Instruments: The Dutch perfected the art of stocks and bonds, giving life to the Amsterdam Stock Exchange.
- Warehouse System: Merchants stored goods in Amsterdam’s vast warehouses, ensuring a reliable supply.
- Stable Government: Political stability provided a hospitable environment for traders and investors alike.
London’s Competitive Advantages
Not far behind, London had unique tricks up its sleeve:
| London’s Strength | Impact |
|---|---|
| Geographical Location | Access to the Atlantic opened London to the New World. |
| The Royal Exchange | Led to financial collaborations that bankrolled trade expeditions. |
| Merchant Navy | A formidable fleet secured trade routes and transported goods. |
| English Law | Contributed to an efficient business landscape. |
With both Amsterdam and London jostling for the top, their trade and finance operations wrote history. Amsterdam’s mature trading network set the standard globally. Contrarily, London’s potential hinted at a future global empire in trade.
Legacy Of Seventeenth Century Trade Dynamos
The seventeenth century was a remarkable era for European cities that became powerhouses of trade and finance. Amsterdam stands out as the champion of economic success during this time. Its influence set the stage for modern finance and left a rich cultural and economic heritage that resonates to this day.
Modern Financial Systems
The foundations of today’s financial systems were laid in these thriving cities. Amsterdam pioneered concepts like the central bank and the stock exchange. These innovations shaped how we conduct trade and manage economies worldwide.
- First stock exchange: The Amsterdam Stock Exchange was established, allowing shares of the Dutch East India Company to be traded.
- Central banking: The Bank of Amsterdam functioned as a proto-central bank, regulating monetary policy.
Cultural And Economic Heritage
Amsterdam’s prosperity spilled into culture, art, and architecture, enriching its historical tapestry. Its wealth from trade led to an explosion of artistic creation and architectural development.
| Cultural Aspect | Impact |
|---|---|
| Golden Age Art | Masters like Rembrandt and Vermeer flourished, funded by wealthy patrons. |
| Architectural Heritage | Grachten houses and the famous canal ring became symbols of Dutch elegance and prosperity. |
Today, these seventeenth-century endeavors continue to shape our world. As trade centers, Amsterdam and its counterparts entrenched practices that became the bedrock of modern finance and left indelible marks on cultural landscapes.
Frequently Asked Questions For Which Of The Following Cities Dominated European Trade And Finance In The Early Seventeenth Century?
Which City Dominated Europe’s Trade And Finance In The Early Seventeenth Century?
Amsterdam dominated Europe’s trade and finance in the early seventeenth century. The city became a pivotal financial center due to its innovative stock exchange and banking system.
What Was A Major Result Of The War Of The Spanish Succession 1701 1713 And The Treaty Of Utrecht 1713 1714?
The Treaty of Utrecht in 1713 ended the War of the Spanish Succession. It resulted in France ceding territory to Britain and Austria, including Newfoundland, and Gibraltar to Britain, marking a shift in the balance of European power.
What Was The Characterization Of England In The Period 1688 1715?
England, during 1688-1715, was marked by political stability, constitutional monarchy establishment, and significant economic growth, signifying the start of modern Britain.
Which Of The Following Was A Major Characteristic Of The English Monarchy In The Eighteenth Century?
The English monarchy in the eighteenth century had limited power due to constitutional developments and parliamentary sovereignty.
Which City Led 17th-century European Trade?
Amsterdam dominated European trade and finance in the early seventeenth century due to its strategic location and progressive financial instruments.
Conclusion
As we’ve journeyed through the annals of history, it’s clear that cities like Amsterdam, Antwerp, and Venice were at the heart of European trade and finance in the seventeenth century. These hubs of commerce set the stage for the economic landscape we know now.
Their stories remind us of the timeless dance between commerce, innovation, and the cities that master them. Let’s embrace these lessons as we navigate the future of trade and prosperity.